Product Risk Assessment Approach
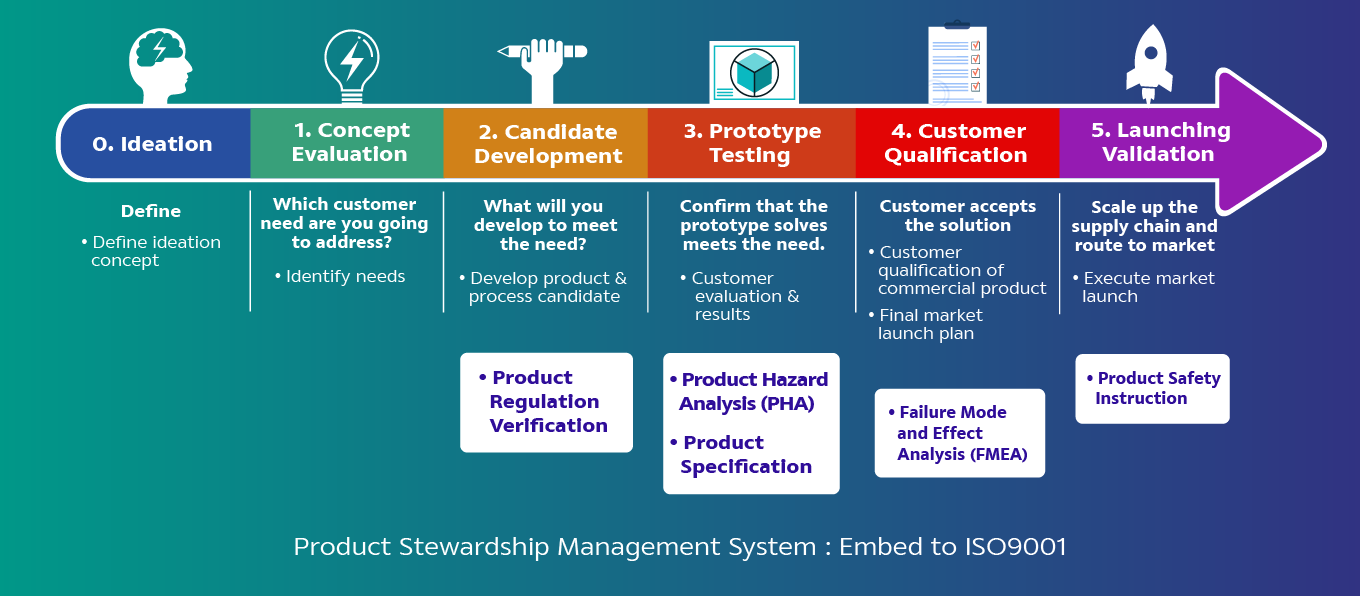
SCGC integrates the Product Stewardship Management System as part of the Quality Management System, In the New Product Development process of SCGC, the Product Risk Assessment starts from the step of Candidate Development until the step of Launching Validation. That approach is to minimize the risks of human and environment through the product life cycle (raw material selection, production, distribution, use, and dispose).
Product Regulation Verification
The company places utmost importance on managing hazardous chemicals in its products to ensure safety and environmental friendliness. The company reviews laws, regulations, and standards related to the cancellation or control of chemical substances, both domestically and internationally, including:
- List of hazardous substances according to the Department of Industrial Works announcement.
- List of hazardous chemicals according to the Ministry of Labor's announcement on welfare and labor protection.
- Ozone-depleting substances under the Montreal Protocol procedure.
- Chemical substances according to Annex XVII of the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH).
- Chemical substances according to the Candidate List of Substance of Very High Concern for Authorization (SVHC).
- Hazardous chemicals under RoHS (The Restriction of Hazardous Substances).
- Chemicals listed in California Proposition 65 to control the use of chemicals throughout the product lifecycle.
Utilize all this information to establish product specifications to ensure the product's quality, safety, health, and environmental standards.
Scope of Assessment
All products of SCGC undergo comprehensive risk assessment throughout their lifecycle aligned with ISO 31000 standards, starting from the selection of raw materials through to disposal. This evaluation encompasses compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, focusing on potential impacts on health, occupational safety, property, and the environment.
Product Risk Assessment Work Through The Product Life Cycle
Methodology and Tools
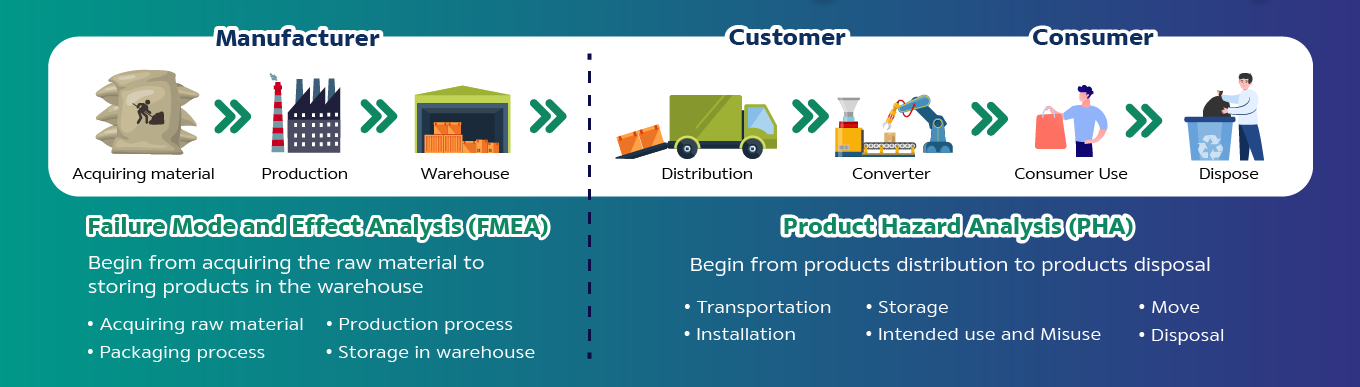
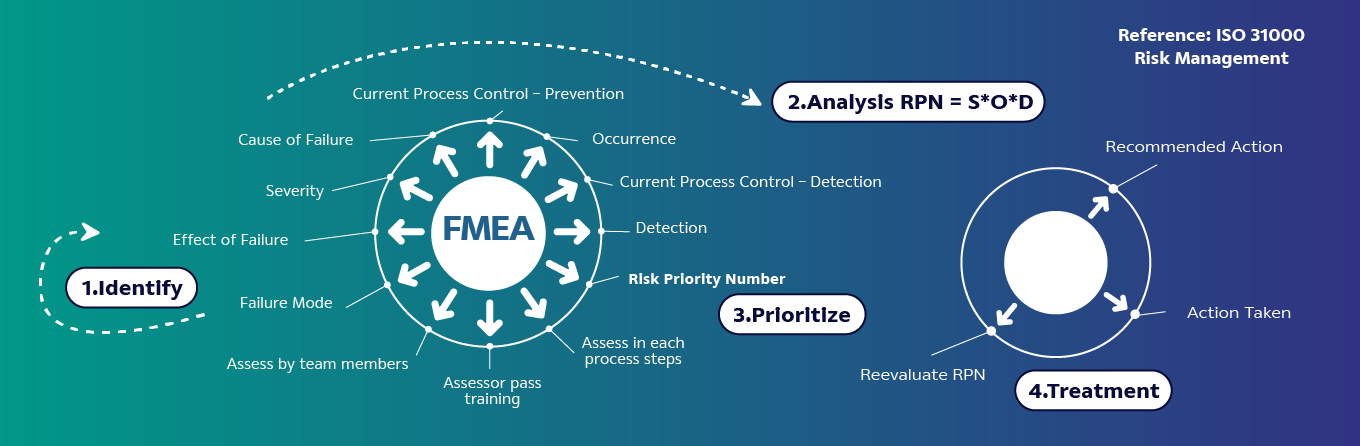
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA): Risk assessment starts from the selection of raw materials through to the storage in warehouses before delivery to customers for use.
- Product Hazard Analysis (PHA): Risk assessment start from delivery of products from the manufacturer to the customer and continues through to disposal.
Steps of Product Risk Assessment
1. Risk identification and impact categories for hazard identification
Risk Identification: Identify potential hazards such as design flaws, manufacturing defects, or risks associated with transportation, storage, handling, usage, and disposal.
- Physical hazards refer to dangers such as explosions, fire, corrosion, and reactive hazards that can cause immediate and severe impacts.
- Chemical hazards refer to dangers arising directly from chemicals or chemical reactions. These chemicals may be present in industrial facilities or workplaces in the form of raw materials, products, emissions, or waste from production processes. For example, contamination by hazardous chemicals listed under REACH and SVHC.
- Health hazards include irritation, carcinogenicity (cancer-causing potential), sensitization, and other health impacts that may take longer to manifest.
- Environmental hazards refer to situations where chemicals leak into water sources, are released into the air, or accumulate in soil and water, entering the food chain and affecting plants and wildlife.
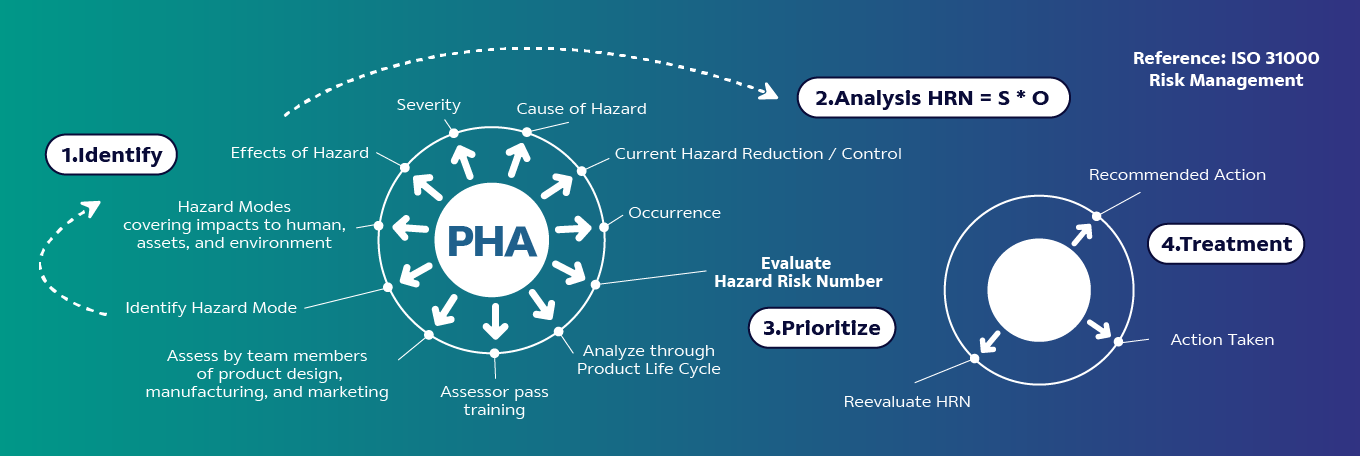
2. 1 Risk Assessment of Product Hazard Analysis (PHA)
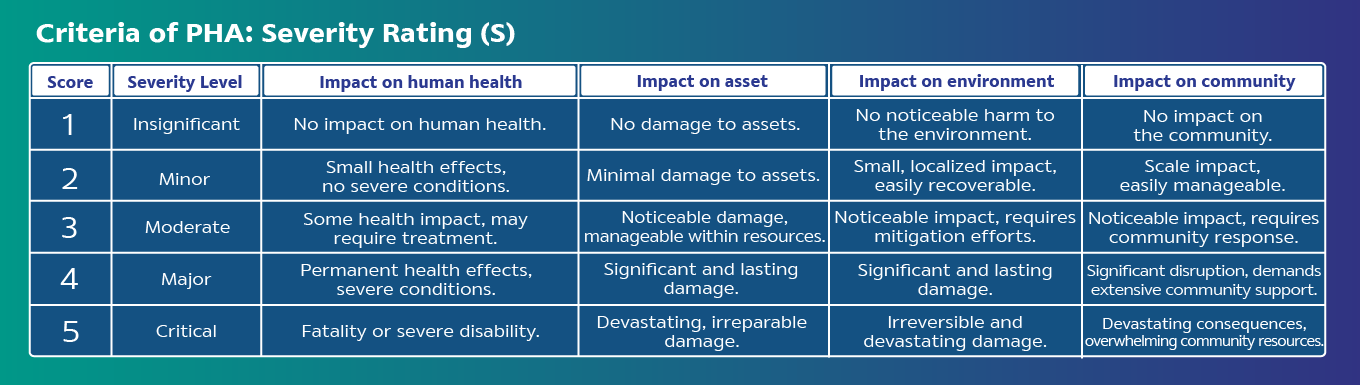
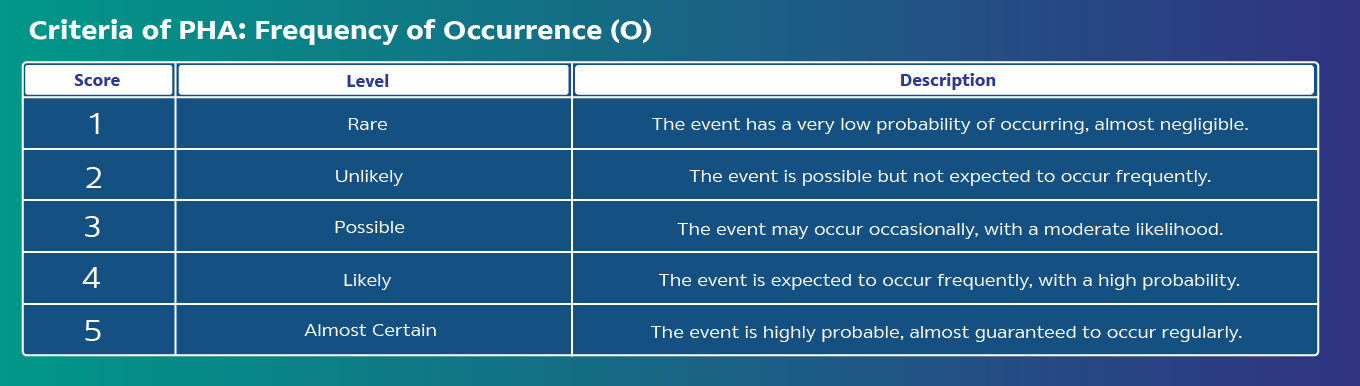
Analyze risk by identifying Severity (S), Cause, and Probability of Occurrence (O), and calculate the Hazard Risk Number (HRN) = S x O for each hazardous issue
2.2 Risk Analysis of FMEA
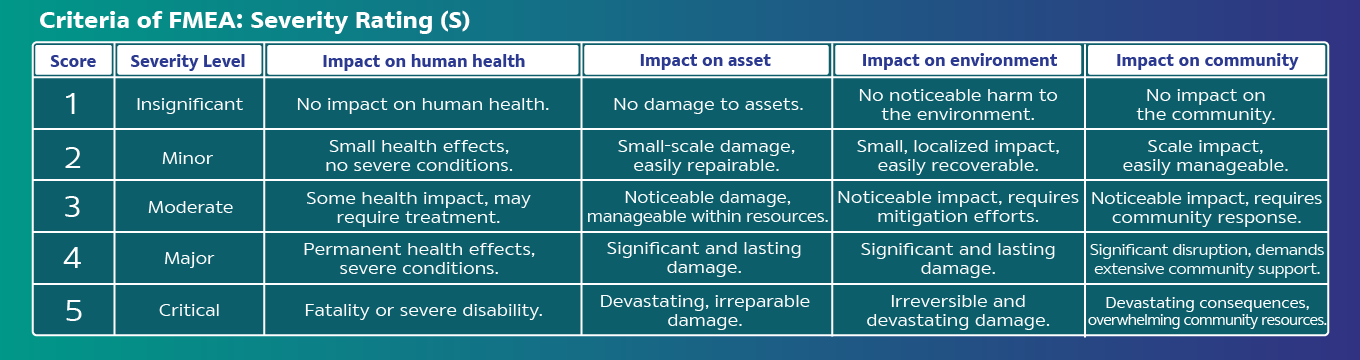
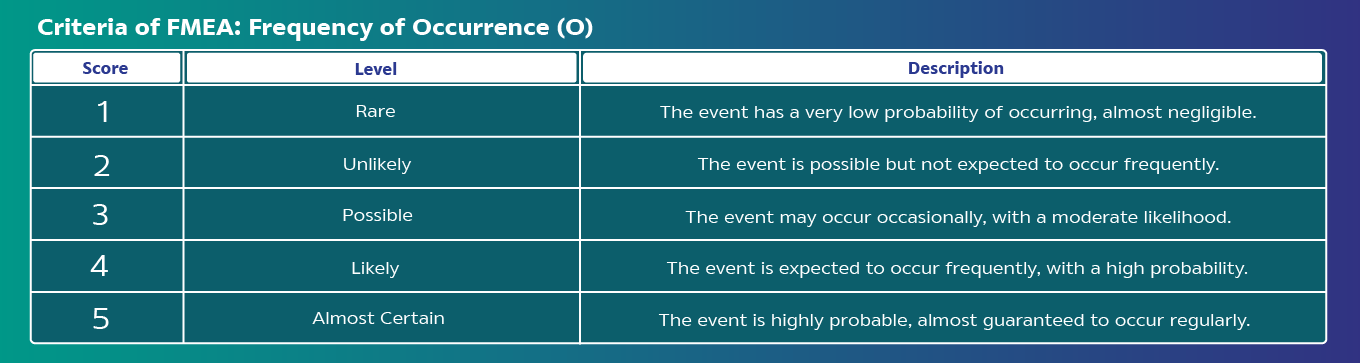
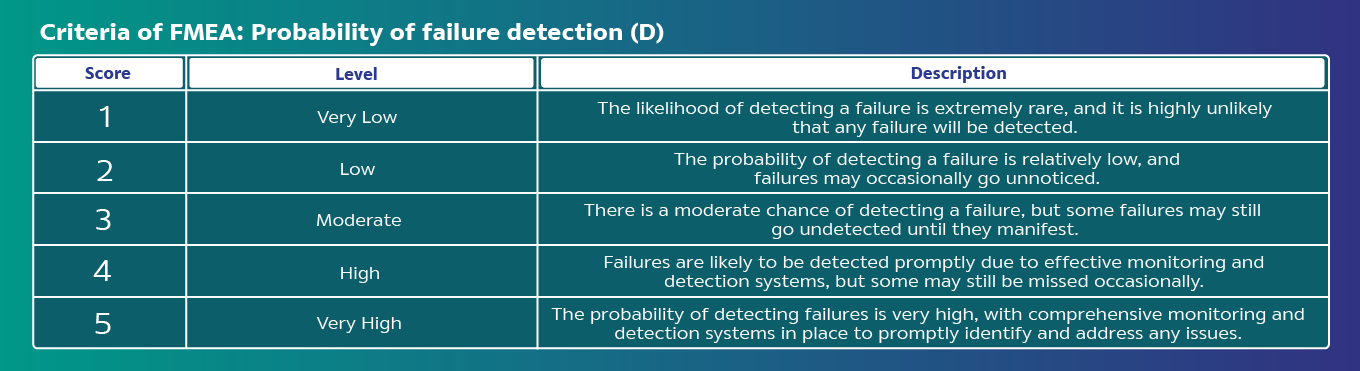
Analyze risk by identifying Severity (S), Cause, Probability of Occurrence (O), and Detection Capability (D), and calculate the Hazard Risk Number (HRN) = S x O x D for each hazardous issue."
3. Risk Prioritization
Prioritize the importance of risks based on HRN analysis scores, with risks having an HRN higher than specified thresholds requiring risk treatment
4. Risk Treatment
When encountering unacceptable risks, it's crucial to mitigate and manage them by implementing preventive measures, conducting risk reassessment post-implementation to ensure they're at acceptable levels. This includes redesigning, providing product specifications, developing product safety instructions according to the GHS (Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals), and communicating this information to employees and partners to ensure safe and environmentally friendly product use.
Example of Product Safety Instruction
----------------------------------------------------------
Product Hazard Analysis (PHA)
Product Hazard Analysis (PHA) is a tool of the risk management, starting from identifying, analyzing, prioritizing risks, then risk treatment. The process covers the product life cycle of transportation, storage, move, installation, intend use and misuse, and disposal. Analyze hazard impacts to human, assets, and environment.
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) Process
FMEA is a tool of the risk management in production process, starting from identifying, analyzing, prioritizing risks, then risk treatment. The process covers the product life cycle of acquiring raw material, production, packaging, and storage. Analyze hazard impacts to quality, safety, health, and environment.